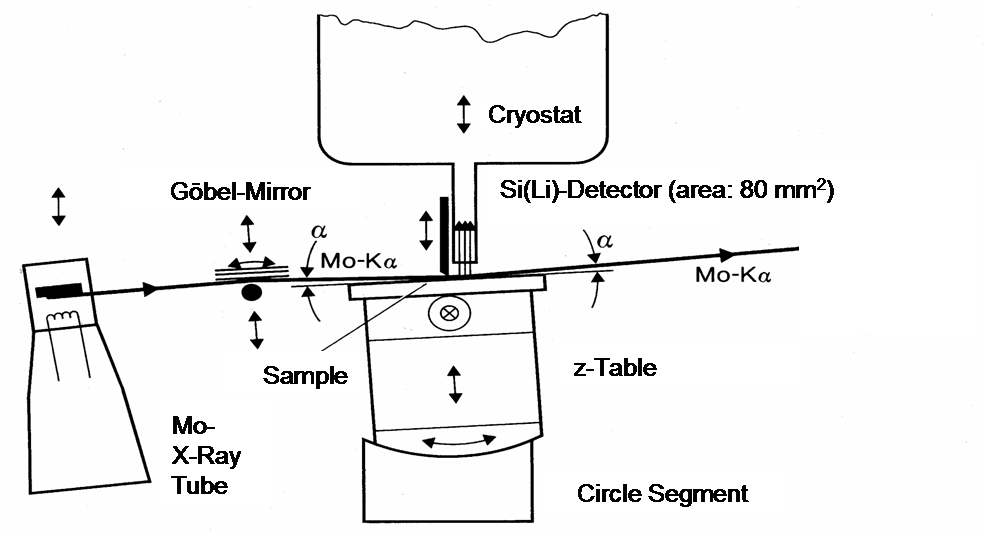
TOTAL-REFLECTION X-RAY FLUORESCENCE (TXRF) SPECTROMETER

Total-Reflexion X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer with monochromatic excitation.
General Description
In X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Analysis samples are irradiated with x-rays leading to the emission of an element specific fluorescence radiation. The photon energy and intensity are typical for the elements and their concentration in the sample. In contrast to the normal XRF analysis, where the information depth is controlled by the mass absorption of the primary beam and the excited fluorescence radiation, the TXRF Analysis uses the external total reflection of the incident beam on a flat sample surface to make the method surface sensitive. The information depth is therefore limited to a few atomic layers, corresponding to the exponential decrease of the evanscent beam occuring under total reflection. The high excitation wavefield at the critical angle makes the method extremely sensitive to surface contaminations down to concentrations below 1010 atoms/cm² (=10 ppm of an atomic monolayer). The main application field of the method is the identification of surface contaminations on semiconductor surfaces under clean room conditions, but also the identification of metal pollutions in waters, air and soil for environmental studies.
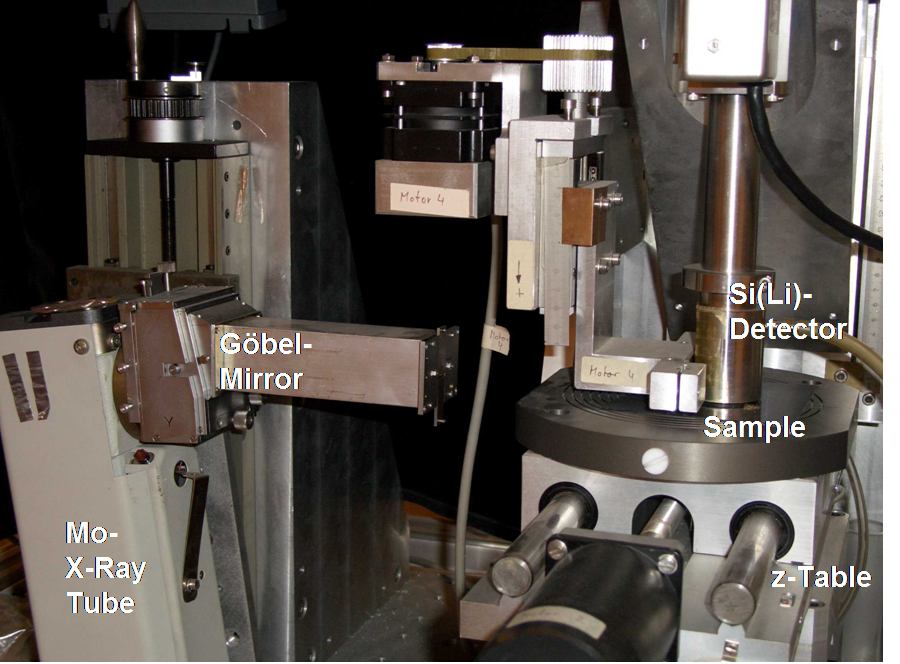
Total-Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer.
Characteristics
| • | Total-Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer (Siemens) with Si(Li)-detector (Tracor) |
| • | Element area: Aluminium to Transurane |
| • | Resolution: all elements |
| • | Energy resolution: typ. 154 eV |
| • | Detection limit: min. 2 * 1010 atoms/cm² |
| • | Accuracy: typ. 10 % |
| • | Information depth: 1 nm bis 3 nm |
| • | Position resolution / sensitivity: 10 mm |
| • | Excitation radiation: Mo-Kα, Cu-Kα |
| • | Samples: reflecting flat samples (wafer, glass) (no sample prepatation), dimensions: max. Ø 150 mm, thickness max. 50 mm, measuring area: Ø 10 mm |
Applications
Trace analysis for heavy metal pollution
in enviromental studies
Wafer surface contamintions in semicoductor industry, especially in combination with Vapor
Phase Decomposition (VPD) accumulation
| Example 1: | Metallic contamination on a Si-wafer surface (test wafer for calibration purpose). |
| Example 2: | Comparison of metal contaminations from top to bottom: fresh current water (Tirolian Ache), standing water (nature, Lake Chiemsee), pond (city, Munich), water from tap (Munich). |
Example 1: Metallic contamination on a Si-wafer surface (test wafer for calibration purpose).
Example 2: Comparison of metal contaminations from top to bottom: fresh current water (Tirolian Ache), standing water (nature, Lake Chiemsee), pond (city, Munich), water from tap (Munich).